
Inputlookup- It is used for searching the contents of a specific lookup table and taking input.Here are the differences between Inputlookup and Outputlookup commands. Splunk lookup commands are used for the retrieval of specific fields from an external file for deriving the value of an event. What do you mean by the Lookup command? State difference between Inputlookup and Outputlookup commands. For example, you can use ‘rex’ and define specific fields in an email ID, which will allow you to differentiate the domain, company, and user ID elements in the email ID.ĥ. Rex- The ‘rex’ command is used for the extraction of specific data or fields from the events.It also helps you find matching conditions for different active nodes that run a particular application.
However, with the ‘where’ command, you can carry out a more in-depth investigation.

When you use the ‘search’ command, it retains search results that have a successful evaluation. Where- The ‘where’ command is used for filtering out the results with the help of ‘eval’ expressions.You can also limit the results when using this command. This can be carried out in several ways, such as ascending order, descending order, and reverse order. Sort- With the Sort command, you can sort the search results for the specified fields.You can use various functions, such as wildcards, quoted phrases, keywords, and value or key expressions for retrieving the events. Search- Search is used for the retrieval of events from indexes and filtering the results that come out in the previous search command.Name the commands included in the “filtering results” category.įollowing are the commands that are included in the “filtering results” category. Eventstats- While the Eventstats command is quite similar to the stats command in certain ways, what differentiates it from stats command is that it calculates the aggregate results inline to every event.Ĥ.These values are then stored in fields that are created newly. Stats- Stats is a command that helps with the calculation of the statistics for each field in your events or search results.Here’s how stats and eventstats are different from each other. Anomalies- When calculating the “unexpected” score for a specific event, you use the command anomalies.ģ.Rename- This command is used for renaming a specific field, and you can also choose multiple fields to run this command with the help of wildcards.Typer- It helps with calculating the eventtype field for search results that match a certain type of event.When the list of fields is not mentioned, you can apply Filldown to all the fields. Filldown- When you need to replace a set of NULL values with the last non-NULL value for a specific field, you can use the Filldown command to achieve the result.Accum- Accum is the command that helps calculate the accumulated sum of a numerical field.Addtotals- Addtotals is used for summing up the numerical fields, and it also allows you to specify only certain fields to sum up instead of calculating the sum for every field.

Abstract- It is used for displaying a brief summary of the text of the search results, which is carried out by creating a summary version of the text rather than displaying the original text.Here are some important search commands that are available on Splunk. Name a few important Splunk search commands. Cluster: When you need to create a cluster or group of similar events, you can use the cluster command.Ģ.Rare: When you use rare, it displays the least common values in a field.Tags: Tags as a command allows users to annotate fields that are specified in your search results.
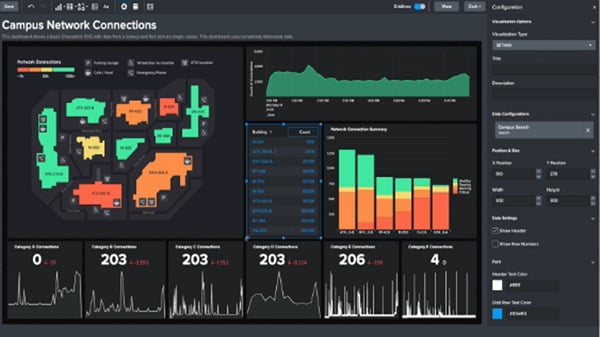
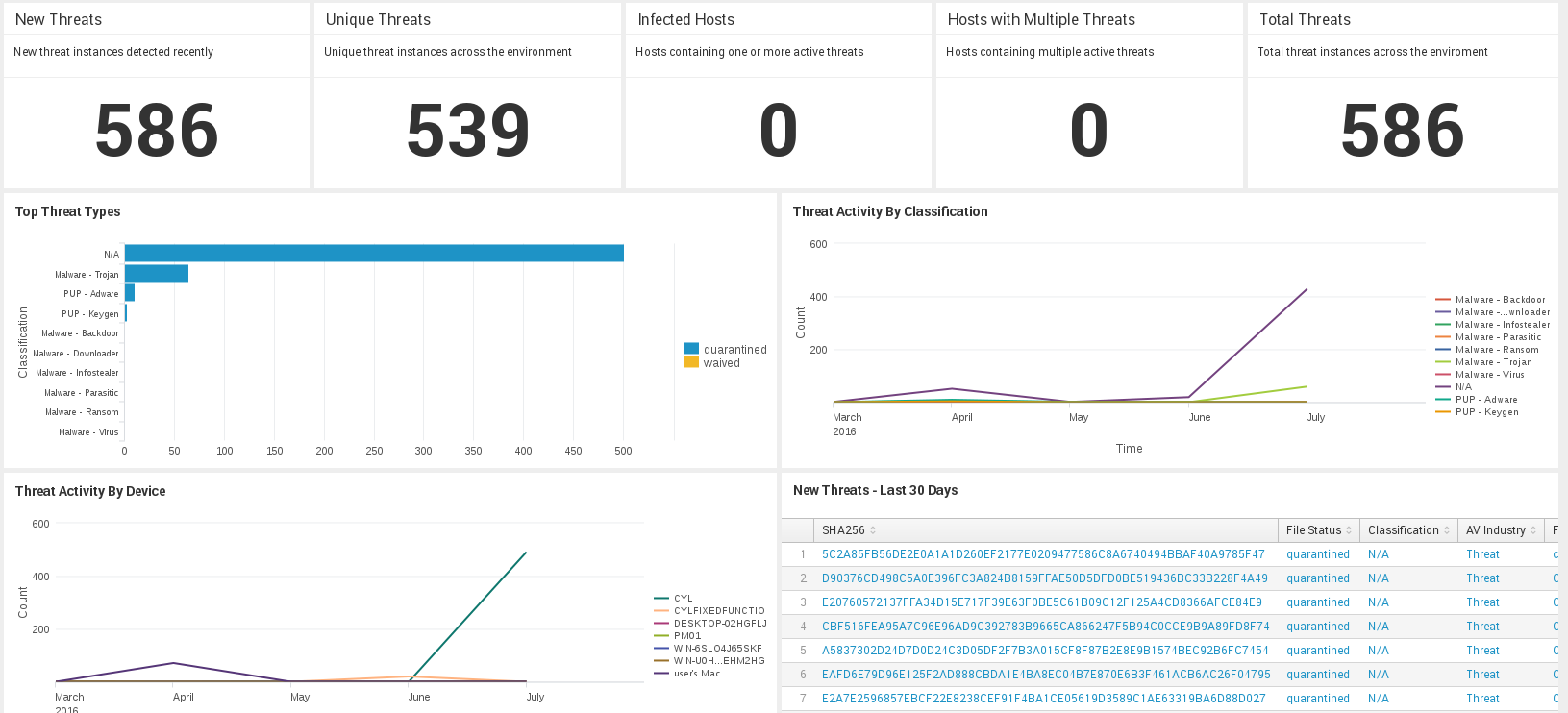
#Splunk dashboard interview questions series


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
